Rendering

Efficient Acquisition of Light Transport Based on Separation of Direct and Global Components
A method for acquiring light transport of a scene based on separation of direct and global illumination components.
Keiichi Ochiai NTT DOCOMO, INC Norimichi Tsumura Toshiya Nakaguchi Yoichi Miyake Chiba University

Curling and Animating Fur Using the Layered-Textures Method
This extension of previous methods for fur rendering based on texture layers adds physically based strand animation and fur shape control.
Paulo Teixeira da Silva Tsuneya Kurihara Tomoyuki Nishita The University of Tokyo

GPU-Accelerated Isosurface Volume Rendering Using Depth-Based Coherence
A novel GPU-based system that permits real-time visualization of isosurfaces in volume data. Depth-based coherence is used to speed up rendering during rotation.
Colin Braley Robert Hagan Yong Cao Denis Gracanin Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University

A Tone-Reproduction Operator Accounting for Mesopic Vision
A tone-mapping operator for mesopic vision in which chrominance changes are perceptually uniform, decoupled from the luminance compression stage and suitable for real-time purposes.
Michihiro Mikamo Marcos Slomp Toru Tamaki Kazufumi Kaneda Hiroshima University
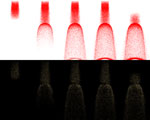
Granular Materials Rendering Based on Radiance Caching
A method for rendering granular materials that models the object as discrete partilces and calculates light scattering with radiance caching.
Toshihisa Yamahata Nara Institute of Science and Technology

Non-Parametric BRDFs for Pearlescent Coatings
An optimal BRDF model that uses a non-parametric model to represent the color-shift effect of pearlescent coatings, which are widely used in various industrial products.
Myoung Kook Seo Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology

Computer-Generated Tie-Dyeing Pattern
A novel interactive method for simulation of tie-dyeing patterns considering 3D folded-cloth geometry.
Yuki Morimoto Ono Kenji VCAD System Research Program, RIKEN

Photon-Density Estimation Using Multiple-Importance Sampling
Applying multiple-importance sampling to density estimation to reduce photon-map noise. The method is easy to implement, imposes low overhead, and delivers good results without nervous parameter tuning.
Yusuke Tokuyoshi

